

Knee Ligament Injury are among the most common and debilitating setbacks faced by athletes and active individuals. Whether it’s a torn ACL or a sprained MCL, these injuries can disrupt daily life and derail athletic aspirations. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the intricacies of knee joint ligament injuries, from their anatomy to treatment options and prevention strategies.
Knee ligament injuries occur when the ligaments in knee injury that stabilize the knee joint are stretched, torn, or otherwise damaged. These ligaments include the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL), posterior cruciate ligament (PCL), medial collateral ligament (MCL), and lateral collateral ligament (LCL). When these ligaments are compromised, it can lead to instability, pain, and reduced range of motion in the knee.
Understanding the anatomy of the knee is crucial in comprehending how ligament injury of the knee occurs. The knee is a complex joint composed of bones, cartilage, tendons, and ligaments. Ligaments play a vital role in providing stability and support to the knee, preventing excessive movement and ensuring proper alignment during activities.
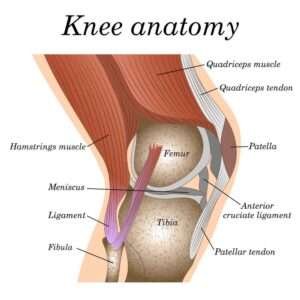
Knee joint ligament injuries can vary in severity and location. classified into various types, are commonly encountered in medical practice. These include:
Each injury has its own set of symptoms and treatment options, depending on the extent of the damage.
Diagnosing a knee ligament injury typically involves a thorough physical examination, including tests to assess stability and range of motion in the knee. Imaging studies such as X-rays, MRI, or CT scans may also be ordered to visualize the extent of the damage and rule out other potential injuries.
The decision to undergo surgery for a knee ligament injury depends on various factors, including the individual’s age, activity level, overall health, and the extent of the injury. While some injuries may heal with conservative measures, others may require surgical intervention to restore stability and function to the knee.
Rehabilitation is crucial for recovery, focusing on strengthening muscles, improving flexibility, and restoring range of motion. Physical therapy, coupled with modalities like ultrasound or electrical stimulation, aids in the healing process. For ligament tear treatment, rehabilitation procedure is key to successful recovery.

Preventing knee ligament injuries involves adopting proper techniques and precautions during physical activities, including warm-up exercises, stretching, and wearing appropriate footwear and protective gear. Strengthening the muscles around the knee through targeted exercises can also help reduce the risk of injury.
In conclusion, knee ligament injuries can be challenging to overcome, but with proper diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation, individuals can regain mobility and function in their knees. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for knee ligament injuries, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their knee health and prevent future injuries.
For further information and guidance on knee ligament injuries, consult with a qualified healthcare professional, such as Dr. Bakul Arora, who specializes in orthopedic care and sports medicine.
In summary, knee ligament injuries are complex and require comprehensive evaluation and treatment to achieve optimal outcomes. By arming yourself with knowledge and seeking timely medical intervention, you can navigate the challenges of knee ligament injuries and embark on the path to recovery.
Knee ligament injuries often occur during sports activities that involve sudden stops, changes in direction, or direct blows to the knee. Accidents, falls, and overuse can also lead to ligament tears.
Symptoms of a knee ligament injury include pain, swelling, instability, difficulty bearing weight on the affected knee, and a popping sensation at the time of injury.
While it’s not always possible to prevent knee ligament injuries, certain measures can help reduce the risk, such as warming up before exercise, using proper technique during sports activities, wearing appropriate protective gear, and maintaining strong muscles around the knee through regular exercise.
Untreated knee ligament injuries can lead to chronic pain, instability, and an increased risk of future knee injuries. They may also contribute to the development of osteoarthritis in the affected knee joint over time.
The timing of return to sports or physical activities depends on the severity of the injury, the chosen treatment, and the individual’s progress during rehabilitation. It’s essential to follow the guidance of a healthcare professional and gradually reintroduce activities to prevent re-injury.
Your healthcare provider can offer personalized advice and treatment recommendations for knee ligament injuries. Additionally, reputable medical websites, orthopedic associations, and sports medicine organizations provide valuable resources and information on prevention, treatment, and recovery.
WhatsApp us